Mastering bilingual Google Ads campaigns is the ultimate competitive advantage in the Canadian market. While most advertisers struggle with proper implementation, this guide reveals proven strategies for creating high-performing campaigns that effectively target both English and French-speaking Canadians without doubling your workload or budget.
Language Landscape
Understanding Canada's linguistic demographics is crucial for effective campaign structure. According to Statistics Canada:
French is the first official language for 22.8% of Canadians
17.9% of Canadians are bilingual in English and French
Quebec is 85% French-speaking
Significant French-speaking populations exist in New Brunswick, Eastern Ontario, and parts of Manitoba
The implications for Google Ads campaigns are significant: targeting by language alone is insufficient, as geographic and language factors must work together for optimal results.
Campaign Structures
There are three main approaches to structuring bilingual campaigns in Canada:
Separate Campaigns
Best for: Brands with distinct positioning or offerings in each language market
Structure:
English Canada Campaign
French Canada Campaign (primarily Quebec)
French minority regions as optional third campaign
Advantages:
Complete budget control between language markets
Ability to create distinct messaging and offers
Simplified management of ad assets
Disadvantages:
Potential audience overlap
Higher management overhead
Possible keyword competition between campaigns
Single Campaign Approach
Best for: Smaller businesses or those with limited management resources
Structure:
One campaign targeting all of Canada
Ad groups divided by language
Language targeting applied at the ad group level
Advantages:
Simplified campaign management
Unified budget across language markets
Easier performance comparison
Disadvantages:
Less control over budget allocation between languages
Potential for improper ad serving without careful setup
Limited ability to tailor bidding strategies by language
Hybrid Approach
Best for: Sophisticated advertisers seeking maximum control
Structure:
English campaign targeting English Canada (excluding Quebec)
French campaign targeting Quebec
Bilingual campaign targeting bilingual regions with both language ad groups
Advantages:
Precise control over geographic and linguistic targeting
Optimal budget allocation
Prevention of language mismatch situations
Disadvantages:
Most complex to manage
Requires sophisticated tracking setup
Higher potential for targeting errors
Keyword Strategy
Effective keyword strategy goes beyond simple translation. Here's a systematic approach:
Translation Considerations
Direct Translation Pitfalls:
Many technical terms have different usage patterns in Canadian French vs. European French
Direct translations often miss cultural context and colloquialisms
Search volume can vary dramatically between translated terms
Recommended Process:
Begin with top-performing English keywords
Use professional translation with Canadian French context
Validate with native Quebec French speakers
Use Google's Keyword Planner to check actual search volumes for each variant
Identify Quebec-specific terms without English equivalents
Volume Variations
Based on my experience running bilingual campaigns across Canada, expect these patterns:
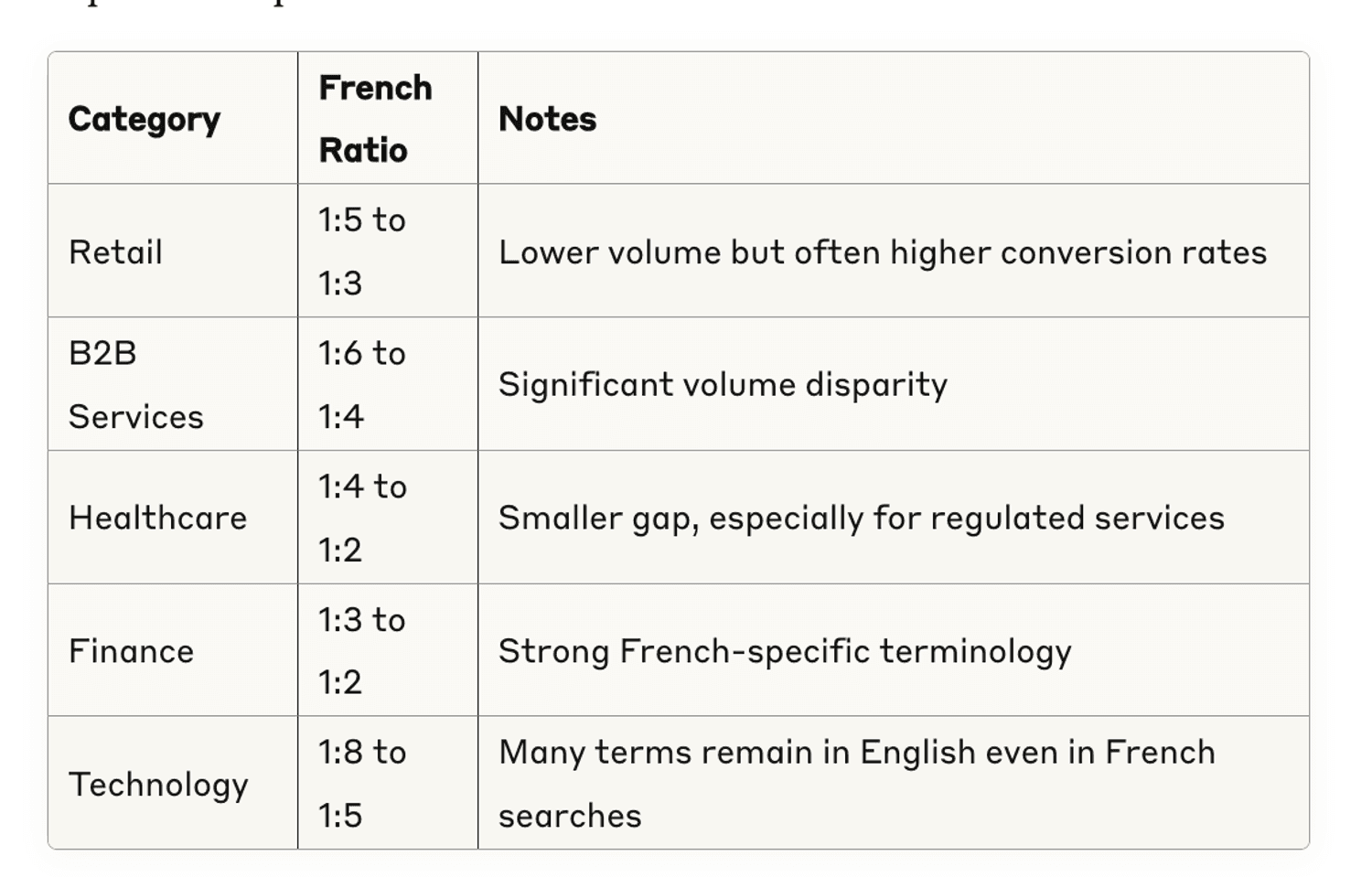
These ratios help set realistic expectations for French campaign performance and budget allocation.
Ad Copy Optimization
Creating effective ad copy for bilingual campaigns requires more than translation:
Cultural Nuances
Key Differences:
Quebec consumers typically respond better to relationship-focused messaging rather than direct offers
Social proof carries more weight in French Canadian advertising
Humor and cultural references often need significant adaptation
Direct calls-to-action may need softening in French
Character Limits
French typically requires 15-25% more characters than English for the same message. Navigate this by:
Creating message concepts in French first, then adapting to English
Using dedicated copywriters for each language rather than translators
Focusing on the core value proposition rather than attempting feature parity
Leveraging Responsive Search Ads to test multiple headline/description combinations
Ad Extensions
Develop distinct extensions for each language:
Different sitelink hierarchies based on language-specific user priorities
Callout extensions addressing unique French Canadian market concerns
Location extensions with appropriate language-specific business names
Structured snippets highlighting features most relevant to each market
Budget Allocation
Budget distribution for bilingual campaigns should be strategic rather than proportional:
Market-Based Strategy
While Quebec represents 22.8% of Canada's population, optimal budget allocation is rarely a direct percentage match. Consider these factors:
Competition levels often differ significantly between language markets
Click costs in French campaigns typically run 10-25% lower than English equivalents
Conversion rates often vary by market segment and language
Seasonality affects language markets differently (especially around Quebec holidays)
Recommended Approach:
Start with population-based allocation (around 20-25% to French campaigns)
Adjust based on initial performance data after 2-3 weeks
Implement regular reallocation based on ROAS rather than fixed percentages
Create separate budget "floors" to ensure minimum presence in both markets
Technical Implementation
Proper technical setup is critical for bilingual campaign success:
Targeting Settings
Critical Settings:
Target French ads to "French" language setting
Target English ads to "English" language setting
Consider adding "Target All Languages" as a supplementary setting for Quebec campaigns (captures users with devices set to English but physically in Quebec)
Landing Page Configuration:
Implement hreflang tags properly:
hreflang="en-ca"andhreflang="fr-ca"Ensure Google's crawlers can access both language versions
Verify browser language detection functions properly
Test landing page load times for both language versions
Tracking Setup
French and English campaigns often show different attribution patterns:
Conversion paths are typically 15-30% longer in French campaigns
Mobile usage patterns differ between language markets
Brand interaction expectations vary culturally
Implementation Recommendations:
Set appropriate conversion windows (consider longer windows for French campaigns)
Implement cross-domain tracking if using separate domains for each language
Create language-specific conversion actions for more accurate tracking
Use Google Tag Manager to ensure consistent event tracking across languages
Performance Benchmarks
Understanding realistic performance differences helps set appropriate goals:
Typical Variations
Based on aggregate data from Canadian bilingual campaigns:
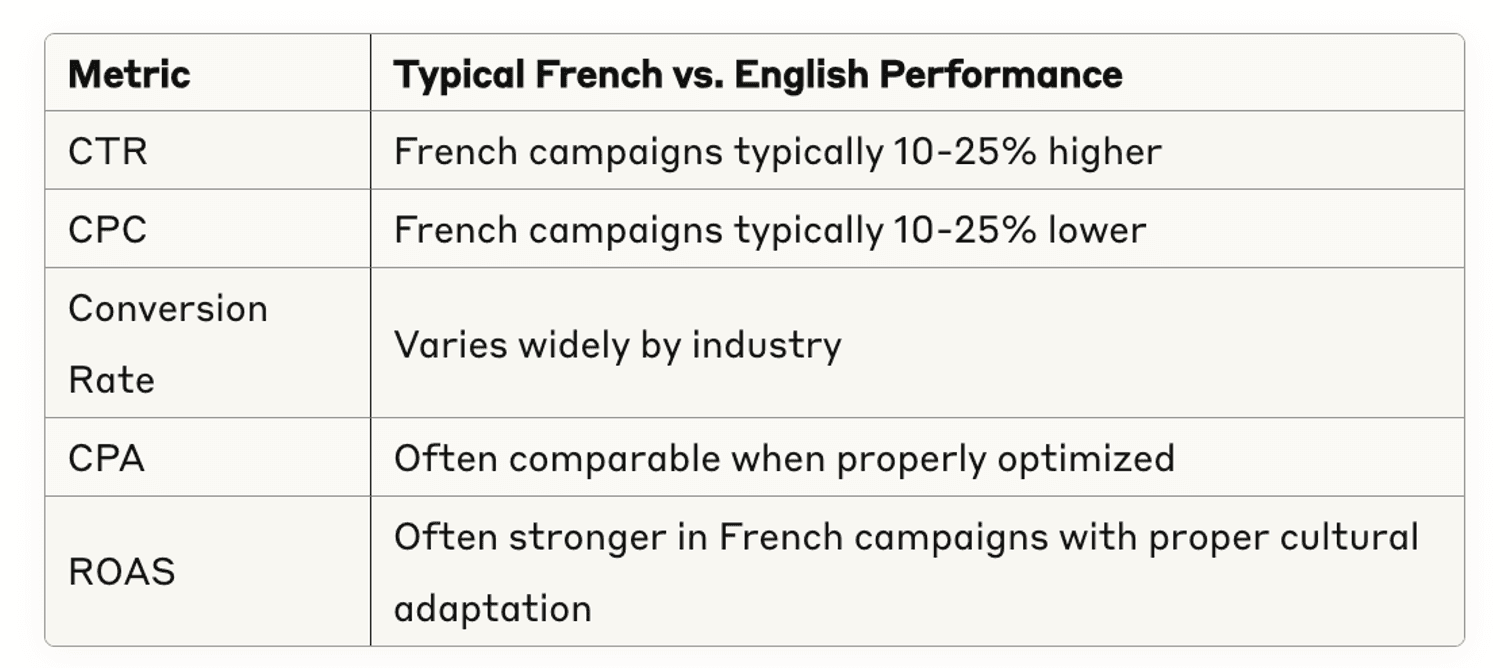
Industry-Specific Insights:
E-commerce: French campaigns often show higher AOV but lower conversion rates
Lead generation: Form completion rates typically higher in English campaigns
B2B: Sales cycle length often differs significantly between language markets
Testing Strategy
Effective optimization requires understanding key differences in how French and English campaigns respond to changes:
Testing Priorities
English Campaigns:
Headline testing usually yields highest impact
CTA variations
Feature emphasis
Social proof elements
French Campaigns:
Value proposition framing often yields highest impact
Relationship/trust elements
Headline testing
Technical/practical details
Bidding Approaches
French campaigns often benefit from different bidding approaches:
Target CPA strategies typically require 20-30% more data to optimize effectively
Manual bidding often outperforms automated strategies in early campaign stages
Maximize Conversions tends to perform better than Target CPA for smaller French campaigns
Consider longer optimization periods for French campaigns before judging performance
Implementation Plan
For advertisers new to bilingual Canadian campaigns:
Month 1: Foundation
Research language-specific keywords and search volumes
Set up separate campaigns with appropriate targeting
Create culturally adapted (not just translated) ad copy
Implement proper tracking for both languages
Allocate initial budgets based on market size and business objectives
Month 2: Optimization
Analyze performance data from both language campaigns
Adjust budget allocation based on initial results
Refine ad copy based on early performance indicators
Expand keyword lists with language-specific terms
Test different landing page approaches for each market
Month 3: Scaling
Implement advanced bidding strategies based on accumulated data
Expand to additional campaign types (Discovery, Video, etc.)
Develop sophisticated audience targeting for each language market
Create new ad variations based on proven messages
Build systematic testing plan for ongoing optimization
Common Pitfalls
Based on my experience with hundreds of bilingual campaigns, these are the most frequent mistakes:
Direct translation without cultural adaptation French Canadian users can quickly identify poorly translated ads, damaging brand perception
Identical campaign structures Search behavior differs significantly between markets, requiring unique keyword organization
Equal budget allocation regardless of performance Budget should flow to performance rather than being artificially constrained by language
Ignoring regional differences within language groups French speakers in New Brunswick have different search patterns than those in Montreal
Insufficient testing of French campaigns Lower volume often leads to neglect of proper testing in French campaigns
Case Study
A national retail chain implemented this bilingual campaign approach with impressive results:
Previous structure: Single campaign with mixed language ads
New structure: Separate campaigns with culturally adapted messaging
Results:
37% increase in French campaign ROAS
24% improvement in overall conversion rates
18% lower CPA across both language campaigns
42% higher CTR in French campaigns
The key success factors were proper cultural adaptation of messaging and allowing performance data to drive budget allocation between language markets.
Conclusion
Effective English-French Google Ads campaigns require more than simple translation—they demand understanding Canada's unique linguistic landscape and creating strategies that respect cultural differences while maximizing performance.
By implementing proper campaign structures, developing language-specific keywords, creating culturally adapted messaging, and optimizing based on performance data rather than assumptions, advertisers can achieve significantly stronger results across both of Canada's official languages.
Remember that bilingual advertising in Canada isn't just about compliance or reaching a broader audience—it's about connecting with consumers in their preferred language with culturally relevant messaging that resonates on a deeper level.
Mastering bilingual Google Ads campaigns is the ultimate competitive advantage in the Canadian market. While most advertisers struggle with proper implementation, this guide reveals proven strategies for creating high-performing campaigns that effectively target both English and French-speaking Canadians without doubling your workload or budget.
Language Landscape
Understanding Canada's linguistic demographics is crucial for effective campaign structure. According to Statistics Canada:
French is the first official language for 22.8% of Canadians
17.9% of Canadians are bilingual in English and French
Quebec is 85% French-speaking
Significant French-speaking populations exist in New Brunswick, Eastern Ontario, and parts of Manitoba
The implications for Google Ads campaigns are significant: targeting by language alone is insufficient, as geographic and language factors must work together for optimal results.
Campaign Structures
There are three main approaches to structuring bilingual campaigns in Canada:
Separate Campaigns
Best for: Brands with distinct positioning or offerings in each language market
Structure:
English Canada Campaign
French Canada Campaign (primarily Quebec)
French minority regions as optional third campaign
Advantages:
Complete budget control between language markets
Ability to create distinct messaging and offers
Simplified management of ad assets
Disadvantages:
Potential audience overlap
Higher management overhead
Possible keyword competition between campaigns
Single Campaign Approach
Best for: Smaller businesses or those with limited management resources
Structure:
One campaign targeting all of Canada
Ad groups divided by language
Language targeting applied at the ad group level
Advantages:
Simplified campaign management
Unified budget across language markets
Easier performance comparison
Disadvantages:
Less control over budget allocation between languages
Potential for improper ad serving without careful setup
Limited ability to tailor bidding strategies by language
Hybrid Approach
Best for: Sophisticated advertisers seeking maximum control
Structure:
English campaign targeting English Canada (excluding Quebec)
French campaign targeting Quebec
Bilingual campaign targeting bilingual regions with both language ad groups
Advantages:
Precise control over geographic and linguistic targeting
Optimal budget allocation
Prevention of language mismatch situations
Disadvantages:
Most complex to manage
Requires sophisticated tracking setup
Higher potential for targeting errors
Keyword Strategy
Effective keyword strategy goes beyond simple translation. Here's a systematic approach:
Translation Considerations
Direct Translation Pitfalls:
Many technical terms have different usage patterns in Canadian French vs. European French
Direct translations often miss cultural context and colloquialisms
Search volume can vary dramatically between translated terms
Recommended Process:
Begin with top-performing English keywords
Use professional translation with Canadian French context
Validate with native Quebec French speakers
Use Google's Keyword Planner to check actual search volumes for each variant
Identify Quebec-specific terms without English equivalents
Volume Variations
Based on my experience running bilingual campaigns across Canada, expect these patterns:

These ratios help set realistic expectations for French campaign performance and budget allocation.
Ad Copy Optimization
Creating effective ad copy for bilingual campaigns requires more than translation:
Cultural Nuances
Key Differences:
Quebec consumers typically respond better to relationship-focused messaging rather than direct offers
Social proof carries more weight in French Canadian advertising
Humor and cultural references often need significant adaptation
Direct calls-to-action may need softening in French
Character Limits
French typically requires 15-25% more characters than English for the same message. Navigate this by:
Creating message concepts in French first, then adapting to English
Using dedicated copywriters for each language rather than translators
Focusing on the core value proposition rather than attempting feature parity
Leveraging Responsive Search Ads to test multiple headline/description combinations
Ad Extensions
Develop distinct extensions for each language:
Different sitelink hierarchies based on language-specific user priorities
Callout extensions addressing unique French Canadian market concerns
Location extensions with appropriate language-specific business names
Structured snippets highlighting features most relevant to each market
Budget Allocation
Budget distribution for bilingual campaigns should be strategic rather than proportional:
Market-Based Strategy
While Quebec represents 22.8% of Canada's population, optimal budget allocation is rarely a direct percentage match. Consider these factors:
Competition levels often differ significantly between language markets
Click costs in French campaigns typically run 10-25% lower than English equivalents
Conversion rates often vary by market segment and language
Seasonality affects language markets differently (especially around Quebec holidays)
Recommended Approach:
Start with population-based allocation (around 20-25% to French campaigns)
Adjust based on initial performance data after 2-3 weeks
Implement regular reallocation based on ROAS rather than fixed percentages
Create separate budget "floors" to ensure minimum presence in both markets
Technical Implementation
Proper technical setup is critical for bilingual campaign success:
Targeting Settings
Critical Settings:
Target French ads to "French" language setting
Target English ads to "English" language setting
Consider adding "Target All Languages" as a supplementary setting for Quebec campaigns (captures users with devices set to English but physically in Quebec)
Landing Page Configuration:
Implement hreflang tags properly:
hreflang="en-ca"andhreflang="fr-ca"Ensure Google's crawlers can access both language versions
Verify browser language detection functions properly
Test landing page load times for both language versions
Tracking Setup
French and English campaigns often show different attribution patterns:
Conversion paths are typically 15-30% longer in French campaigns
Mobile usage patterns differ between language markets
Brand interaction expectations vary culturally
Implementation Recommendations:
Set appropriate conversion windows (consider longer windows for French campaigns)
Implement cross-domain tracking if using separate domains for each language
Create language-specific conversion actions for more accurate tracking
Use Google Tag Manager to ensure consistent event tracking across languages
Performance Benchmarks
Understanding realistic performance differences helps set appropriate goals:
Typical Variations
Based on aggregate data from Canadian bilingual campaigns:

Industry-Specific Insights:
E-commerce: French campaigns often show higher AOV but lower conversion rates
Lead generation: Form completion rates typically higher in English campaigns
B2B: Sales cycle length often differs significantly between language markets
Testing Strategy
Effective optimization requires understanding key differences in how French and English campaigns respond to changes:
Testing Priorities
English Campaigns:
Headline testing usually yields highest impact
CTA variations
Feature emphasis
Social proof elements
French Campaigns:
Value proposition framing often yields highest impact
Relationship/trust elements
Headline testing
Technical/practical details
Bidding Approaches
French campaigns often benefit from different bidding approaches:
Target CPA strategies typically require 20-30% more data to optimize effectively
Manual bidding often outperforms automated strategies in early campaign stages
Maximize Conversions tends to perform better than Target CPA for smaller French campaigns
Consider longer optimization periods for French campaigns before judging performance
Implementation Plan
For advertisers new to bilingual Canadian campaigns:
Month 1: Foundation
Research language-specific keywords and search volumes
Set up separate campaigns with appropriate targeting
Create culturally adapted (not just translated) ad copy
Implement proper tracking for both languages
Allocate initial budgets based on market size and business objectives
Month 2: Optimization
Analyze performance data from both language campaigns
Adjust budget allocation based on initial results
Refine ad copy based on early performance indicators
Expand keyword lists with language-specific terms
Test different landing page approaches for each market
Month 3: Scaling
Implement advanced bidding strategies based on accumulated data
Expand to additional campaign types (Discovery, Video, etc.)
Develop sophisticated audience targeting for each language market
Create new ad variations based on proven messages
Build systematic testing plan for ongoing optimization
Common Pitfalls
Based on my experience with hundreds of bilingual campaigns, these are the most frequent mistakes:
Direct translation without cultural adaptation French Canadian users can quickly identify poorly translated ads, damaging brand perception
Identical campaign structures Search behavior differs significantly between markets, requiring unique keyword organization
Equal budget allocation regardless of performance Budget should flow to performance rather than being artificially constrained by language
Ignoring regional differences within language groups French speakers in New Brunswick have different search patterns than those in Montreal
Insufficient testing of French campaigns Lower volume often leads to neglect of proper testing in French campaigns
Case Study
A national retail chain implemented this bilingual campaign approach with impressive results:
Previous structure: Single campaign with mixed language ads
New structure: Separate campaigns with culturally adapted messaging
Results:
37% increase in French campaign ROAS
24% improvement in overall conversion rates
18% lower CPA across both language campaigns
42% higher CTR in French campaigns
The key success factors were proper cultural adaptation of messaging and allowing performance data to drive budget allocation between language markets.
Conclusion
Effective English-French Google Ads campaigns require more than simple translation—they demand understanding Canada's unique linguistic landscape and creating strategies that respect cultural differences while maximizing performance.
By implementing proper campaign structures, developing language-specific keywords, creating culturally adapted messaging, and optimizing based on performance data rather than assumptions, advertisers can achieve significantly stronger results across both of Canada's official languages.
Remember that bilingual advertising in Canada isn't just about compliance or reaching a broader audience—it's about connecting with consumers in their preferred language with culturally relevant messaging that resonates on a deeper level.



